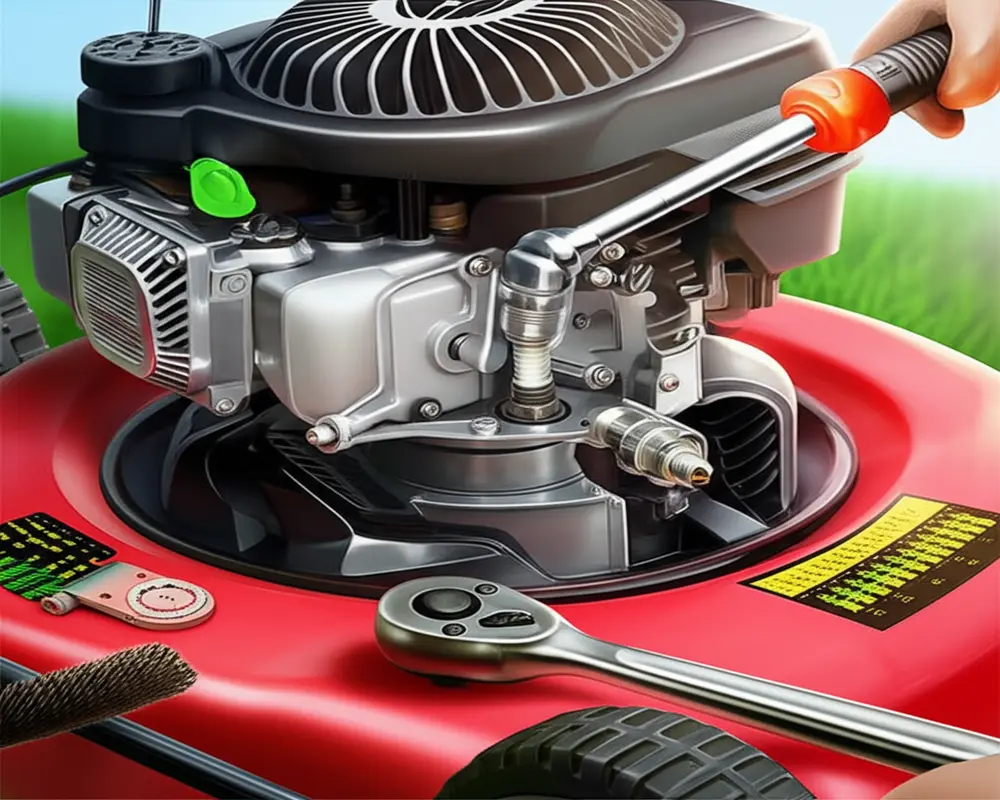
Lawn Mower Spark Plug Replacement: A Complete DIY Guide for 2025
Keeping your lawn mower in peak condition is essential for a healthy, well-manicured lawn. One of the simplest yet most impactful maintenance tasks you can perform is a lawn mower spark plug replacement. This procedure not only improves your mower’s starting ability but also enhances fuel efficiency, smoothens engine operation, and extends the overall engine life. In this comprehensive 2025 guide, you will learn how to expertly replace your lawn mower’s spark plug with clear, safe, and practical steps that anyone can follow.
I. Introduction: Revitalize Your Lawn Mower with a Simple Spark Plug Change
If you notice your lawn mower struggling to start, sputtering during operation, or consuming more fuel than usual, these are classic symptoms of a worn or faulty spark plug. Replacing the spark plug addresses these problems head-on, revitalizing your mower's performance and reliability. Beyond ease of starting, a fresh spark plug contributes to smoother engine running, better fuel economy, and reduced emissions, leading to longer engine life overall.
This guide follows expert principles of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) to ensure you receive safe and reliable maintenance advice that you can trust.
II. Understanding Your Spark Plug: Why It Matters & When to Replace
A. Role of Spark Plug in Combustion
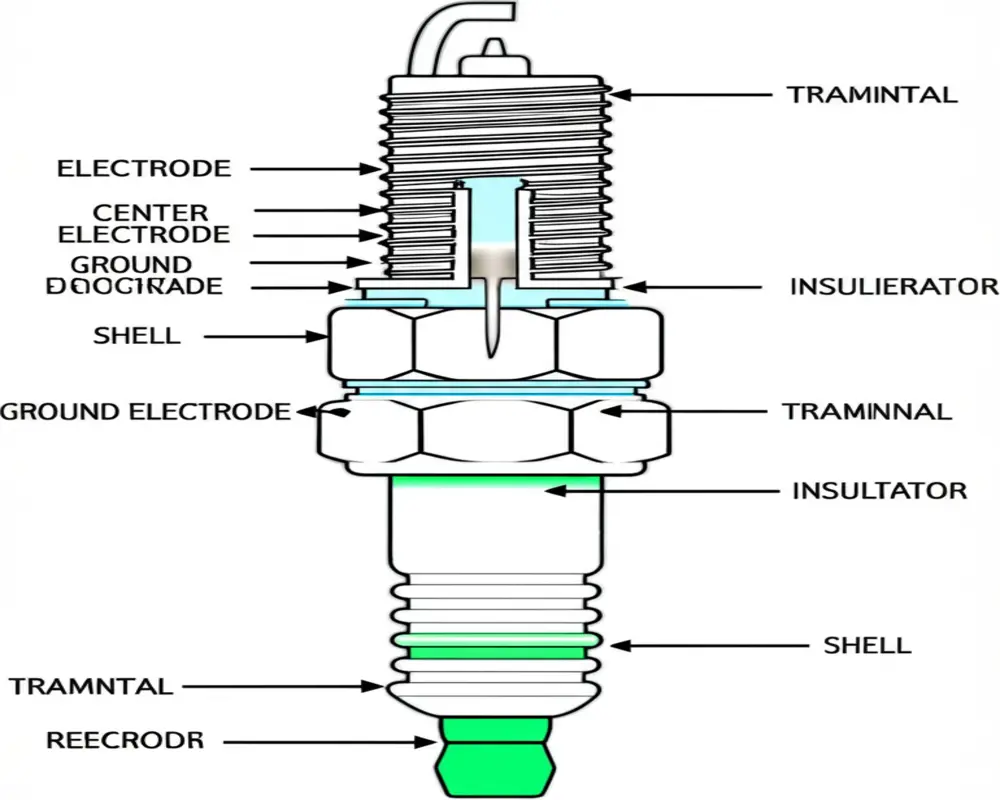
The spark plug is a critical component that initiates combustion in your lawn mower engine. It produces a spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture inside the combustion chamber, enabling the engine to run. Understanding its parts helps in recognizing when replacement is due. A typical spark plug consists of electrodes that conduct electricity, an insulator that isolates the electrical current, and threads that secure it into the engine.
B. Signs of Failing Spark Plug
There are multiple indicators that your spark plug needs replacement:
- Difficulty starting: The mower may require multiple pulls to start or fail to start at all.
- Engine sputtering or misfire: Uneven engine running or stalling can signal spark plug issues.
- Reduced power: Noticeable drop in performance during mowing tasks.
- Increased fuel consumption and exhaust smoke: A fouled spark plug can cause incomplete combustion.
- Visual damage: Carbon fouling, oil deposits, melted or eroded electrodes are visible signs under inspection.
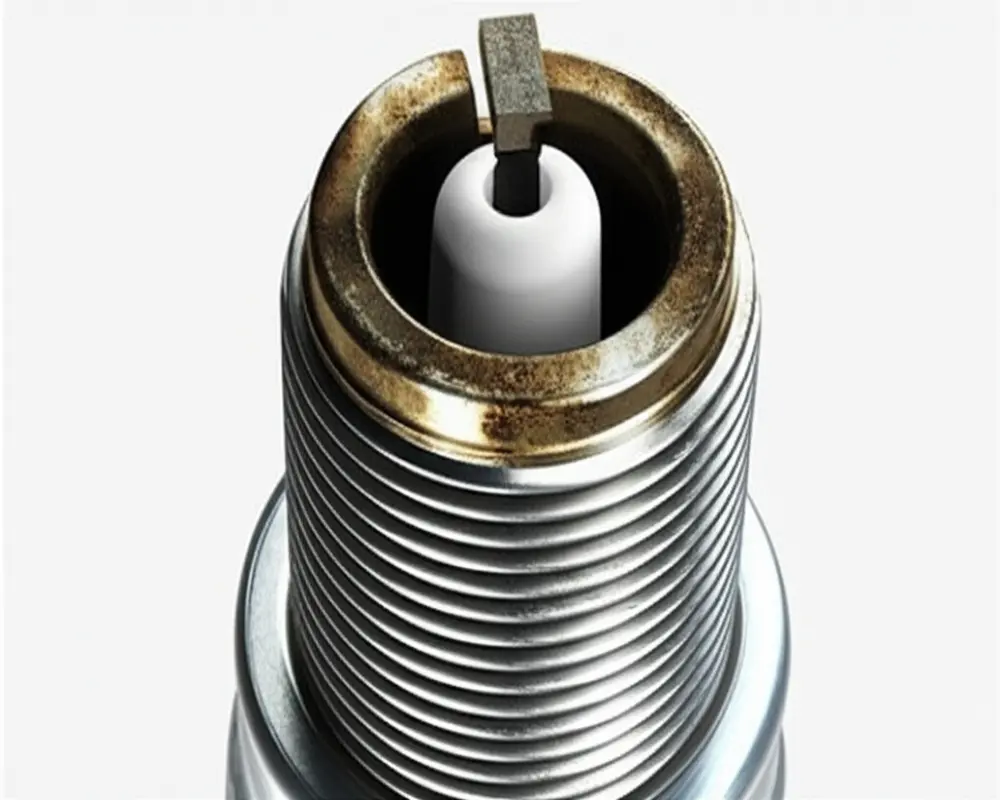

C. Recommended Replacement Intervals
Most manufacturers recommend replacing the spark plug annually or after 25 to 50 hours of operation, whichever comes first. Performing this task seasonally before heavy use is a smart preventive measure to avoid unexpected failures in the middle of your yard work. Following the manufacturer’s guidance helps maintain peak engine health and performance.
III. Choosing the Right Spark Plug: Ensuring Compatibility
A. Finding the Correct Spark Plug Number
Choosing the correct spark plug is crucial for your mower’s engine compatibility and performance. Always start by consulting your mower’s owner’s manual for the recommended spark plug model number. If unavailable, you can read the model number from the existing spark plug or use online lookup tools by entering your mower’s model.
Ensure the spark plug matches these key specifications:
- Thread size
- Reach (thread length)
- Heat range
Using an incompatible spark plug may cause engine damage or poor performance.
B. Spark Plug Types & Gapping
Spark plugs come in various types such as copper, platinum, and iridium. Copper plugs are cheaper and suitable for older mowers, while platinum and iridium offer better durability and performance, ideal for modern engines.
The spark plug gap—the distance between the electrodes—is critical for proper spark generation. Check the recommended gap in your mower manual and measure it using a gap gauge. Adjusting the gap carefully ensures optimal ignition and prevents engine misfires.
IV. Tools and Materials You'll Need
Before starting your lawn mower spark plug replacement, gather the following tools and materials to ensure a smooth and efficient process:
- Spark plug wrench/socket: Common sizes include 5/8 inch and 13/16 inch.
- Spark plug gap gauge: For measuring and adjusting the electrode gap.
- Ratchet and extension bar: To reach tight spots easily.
- Wire brush: For cleaning spark plug threads and surrounding area.
- Compressed air or shop vacuum: To clear debris from the spark plug well.
- Torque wrench: For tightening the spark plug to manufacturer specifications.
- Dielectric grease (optional): Helps ensure a secure electrical connection.
- New appropriate spark plug: Match your mower’s specifications.
- Clean rags or paper towels: To wipe surfaces and hands.

V. Safety First: Important Precautions Before You Start
Safety is paramount when working with power equipment. Follow these precautions before beginning your spark plug replacement:
- Disconnect the spark plug wire: Prevents accidental starting.
- Allow the engine to cool: Avoid burns from hot components.
- Secure mower on level ground: Use wheel chocks or blocks and disable the blade if possible.
- Wear personal protective equipment: Gloves and eye protection safeguard against debris and sparks.
- Handle fuel carefully: If you need to tilt the mower, be cautious of fuel spillage.
VI. Step-by-Step Replacement Guide
Follow these detailed steps to perform your lawn mower spark plug replacement safely and effectively:
- Locate the spark plug: Typically found on the engine cylinder head with a thick ignition wire attached.
- Clean area around spark plug: Use compressed air or a brush to remove dirt and debris.
- Disconnect the spark plug wire boot: Pull firmly but gently to avoid damage.
- Remove the old spark plug: Use the correct socket and wrench to unscrew the plug counterclockwise.
- Inspect the old plug: Check for deposits, wear, or damage as it can diagnose engine issues.
- Prepare the new spark plug: Verify and adjust the gap as per the manual. Optionally, apply a small amount of anti-seize compound on the threads.
- Install the new spark plug: Hand-thread it carefully to avoid cross-threading, then tighten with a torque wrench to the recommended torque.
- Reconnect the spark plug wire: Ensure a secure fit and apply dielectric grease if desired.
- Clean up: Store tools and wipe the work area.
VII. Post-Replacement Checks and First Start-Up
After replacing the spark plug, perform these checks before mowing:
- Confirm the spark plug is tightly secured and the wire connection is firm.
- Clear the work area of tools and debris.
- Start the mower and listen for a smooth engine operation without misfires or unusual noises.
VIII. Common Problems & Troubleshooting
Sometimes, spark plug replacement can present challenges. Here are common issues and how to address them:
- Stripped threads: Avoid overtightening; if stripped, repair with a thread insert kit or consult a professional.
- Broken spark plug removal: Use specialized extractor tools carefully to remove broken parts.
- Difficulty removing old plugs: Apply penetrating oil and allow time before attempting removal again.
- Engine not starting post-replacement: Double-check spark plug gap, wire connection, and ensure the plug is properly tightened.
IX. Maintaining Your Spark Plug & Mower for Longevity
Proper ongoing maintenance enhances spark plug and engine life:
- Regularly inspect and clean the spark plug.
- Follow your mower’s maintenance schedule diligently.
- Use recommended fuel and oil types for your engine.
- Store the mower properly during off-seasons to prevent corrosion.
X. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How often should I change my lawn mower spark plug?
- Typically, every season or after 25 to 50 hours of use, as recommended by manufacturers.
- Can I use car spark plugs in my lawn mower?
- No, lawn mower spark plugs have different specifications and using car plugs can harm your engine.
- What happens if the spark plug gap is incorrect?
- An incorrect gap can cause misfires, hard starting, and poor engine performance.
- Is a torque wrench necessary for spark plug installation?
- Yes, it ensures the plug is tightened to the right specification, preventing damage or loosening.
- Why does my spark plug foul quickly?
- Rapid fouling can result from poor fuel quality, engine oil leaks, or improper air-fuel mixture.
- Can bad spark plugs cause engine damage?
- Yes, prolonged use of faulty plugs can lead to incomplete combustion and potential engine damage.
XI. Conclusion: Enjoy a Smooth-Running Mower
Performing a lawn mower spark plug replacement yourself is a straightforward way to keep your mower running efficiently and reliably. It enhances starting ease, fuel efficiency, and engine performance, saving you time and money on repairs. Regular maintenance fosters longevity and optimal lawn care results. We encourage you to adopt these DIY habits and share your experiences. For more maintenance tips and gardening tool reviews, explore our related guides on lawn mower troubleshooting and best pruning shears.
For additional authoritative information, you may consult the Honda Engines Maintenance Guide and the Briggs & Stratton Spark Plug Tips.

